Composite materials
Materials development and industrialization: new and improved processes and products

Organic matrix composite materials can be defined as a combination of fibrous reinforcements and polymer matrix. Through their properties (good mechanical performances, low density, resistance to corrosion, etc.), these materials help meet today’s societal issues and challenges.
IRT M2P’s composite materials activity was initially structured around high speed processes and the consideration of environmental impacts.
We are now also able to offer a global technological «materials, processes and products» approach adapted to various sectors and markets.
Expertise & Services
- Development of new processes and adaptation/optimization of existing composite processes: volume, net-shape, automation, etc.
- Product development: dimensioning, choice of processes and materials, functionalization
- Contribution to the development of innovative materials (thermoplastics, hybrids, recyclables, etc.)
- Physical process simulation and digital twins
- Health, safety and environmental considerations in materials, process, or product development
- Product and process monitoring, data acquisition and signal processing
- Technical-economical studies and proof-of-concept
- Validation and dimensioning of composite structures
- Pre-production, technological transfer and training
Technology
Preforming
Development and high-volume production of hybrid preforms (multi-material and multistructure)
Preceding step of injection molding or consolidation, preforming can be done with dry materials or prepreg materials Injection
Molding processes
Adapted to thermosets and thermoplastics, RTM or C-RTM processes are mainly used for complex geometries or high-end applications
Compression molding (SMC, BMC)
Pressing semi-finished products to produce high-volume complex parts

Pultrusion
Continuous process for manufacturing composite sections (which can be hollow bodies)
IRT M2P focuses, among other things, on the development of materials, processes and products related to thermoplastic pultrusion

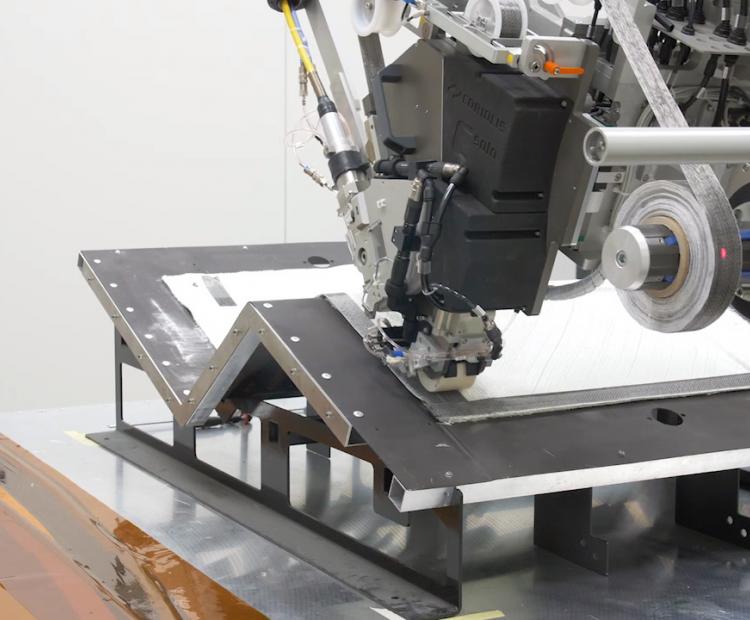
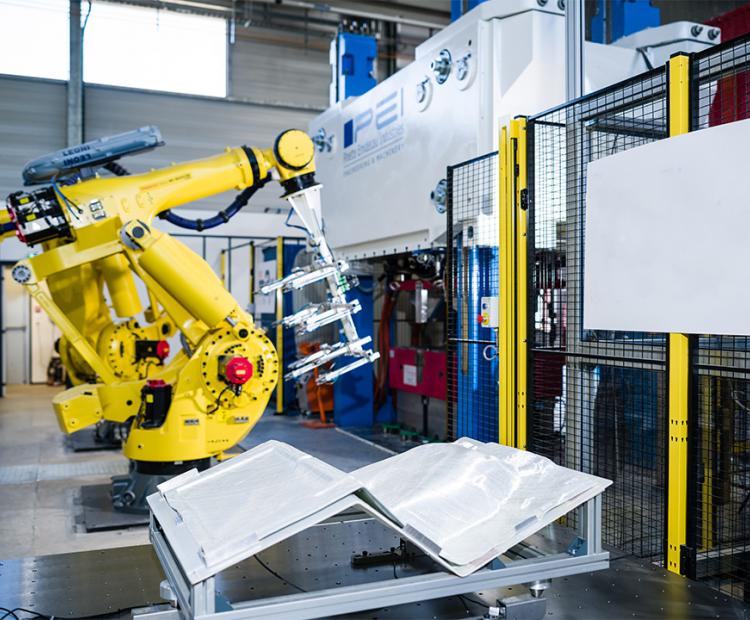
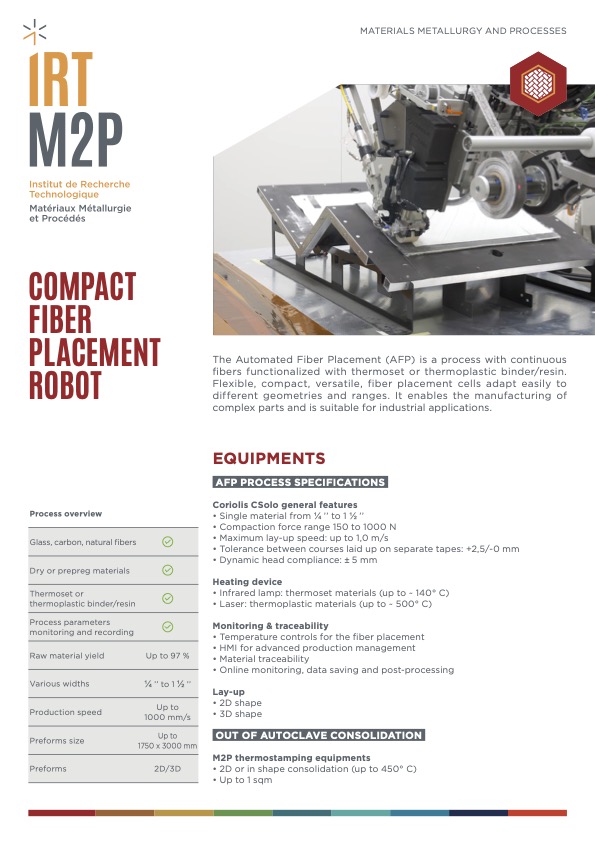
Automated Fiber Placement (AFP)
Sometimes associated with additive manufacturing, this process uses successive draping operations to achieve blanks or 3D parts
Out of autoclave (OoA) thermoforming and consolidation
The shaping and consolidation of thermoplastic materials is a crucial step that confers thermomechanical properties
Manual processes, characterization, and laboratory
Lightweight processes (such as infusion) are widely used for prototyping and manufacturing «small» series of large parts. Coupled with a laboratory environment and characterization, this is an economically attractive and rapid means of implementation
Simulation
Use and development of models and software for process simulation and mechanical design of products
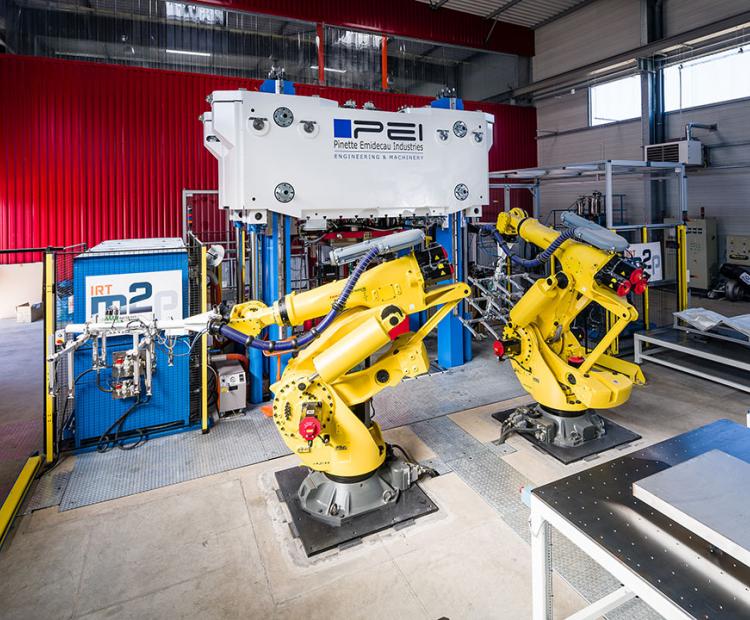
Equipment @M2P
AFP cell
Coriolis C-Solo with laser and IR heating
Hybrid preforming platform
High volume and automated compatible
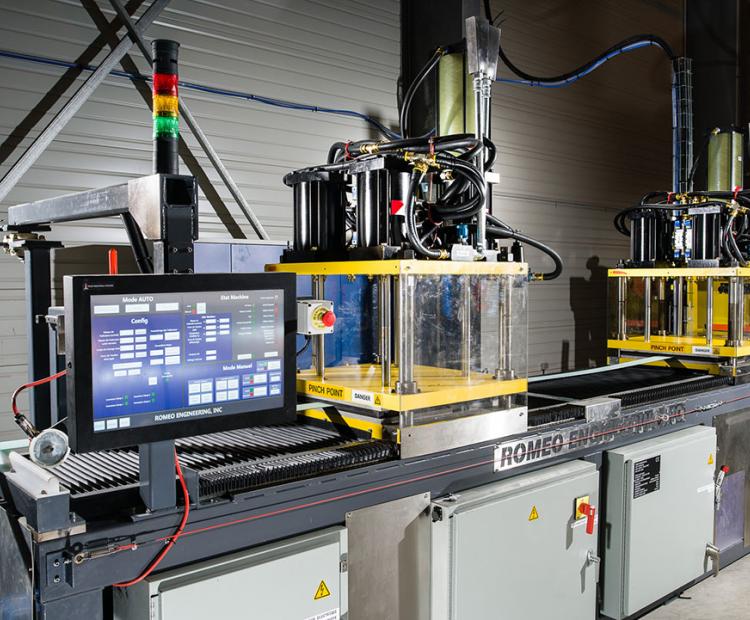
C-RTM platforms
High volume and automated compatible
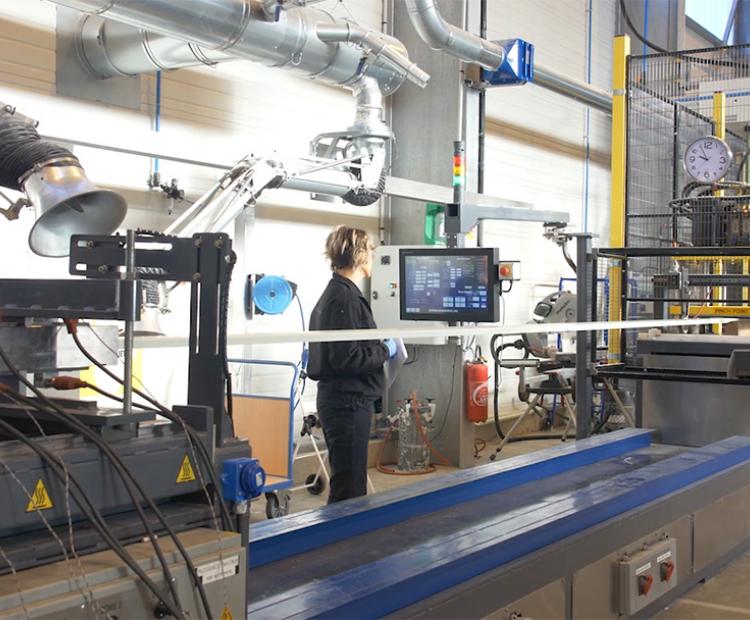
Pultrusion lines
Pulling force from 6 to 12T, speed from 10 to 5000 mm/min
Thermoplastic cell
IR oven & hot plate press (up to 450°C)
Vertical presses
Clamping forces from 180 to 1500 T, platens from 0.25 to 5 m2
Injection & extrusion machines
Single & multi-component, practical and tutorials compatible

Composites workshop
Dedicated to manual processes
Characterization & Laboratory
Hexagon 3D scan
Tools & Molds
From the test piece scale to the : 1 scale demonstrator
APPLICATIONS
Some examples of IRT M2P developments:
- Health and safety improvements to processes in order to limit operator exposure (closed mold processes and automated treatment)
- Innovative thermoplastic resins
- Composite studs for the tunnel industry
- Composite profiles for construction: development of a modular construction system
- Aerospace components reinforced with 3D woven structures
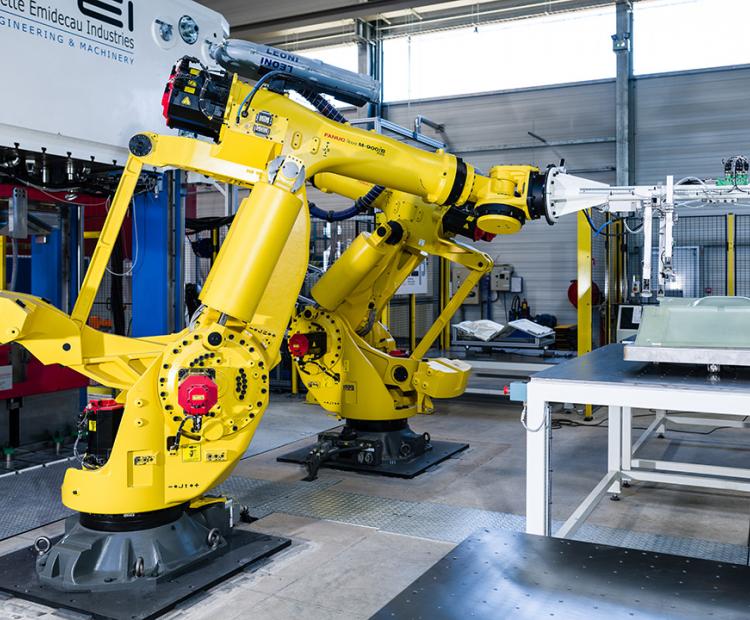
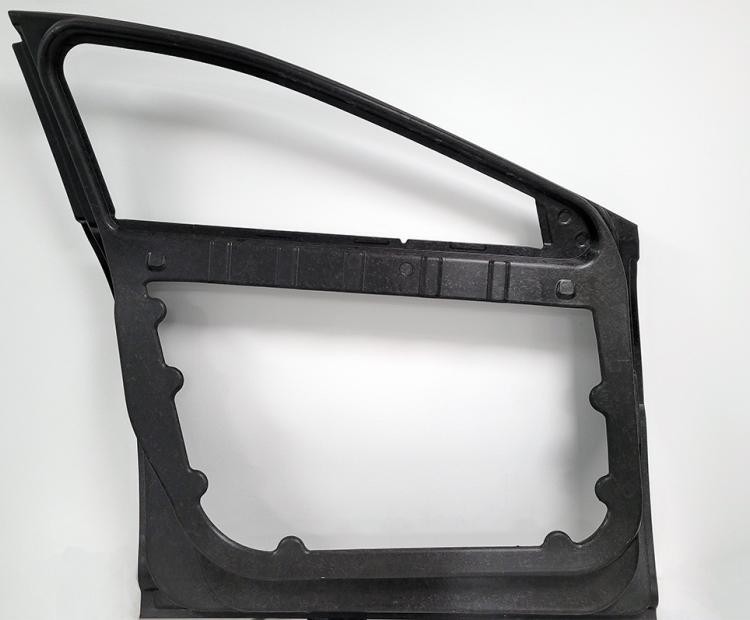
- Automotive components and high-volume automated production

These technological building blocks can be transfered or adapted to other sectors such as transportation, energy, or defense
Do you have a composite project need? Fill out this contact form, and a member of our team will get back to you as soon as possible.